|
Qualification:
- MPhil. 2012 (Biotechnology), PIEAS, Islamabad
- MSc. 2001 (Chemistry) University of Agriculture Faisalabad, Pakistan.
Research Interest
1) To achieve scientific understanding of the metabolism of pesticides by microorganisms.
2) To develop methods to accelerate these metabolic processes for the bioremediation of contaminated soils, sediments, and groundwater.
3) To develop inocula for bioremediation/phytoremediation of pesticides contaminants
Projects:
- Inocula development for biodegradation of pyrethroid insecticides in liquid culture and cotton vegetated soil" 2018-2021 (1.5 M) funded by HEC (NRPU)
- Biodegradation of organophosphate pesticides in liquid culture and soil under influence of different environmental conditions 2010-1013. (US $ 11,500/-)(PI) funded by IFS (International foundation for Science)
Research Activities
Residual analysis of pesticides by HPLC and FTIR analysis
|
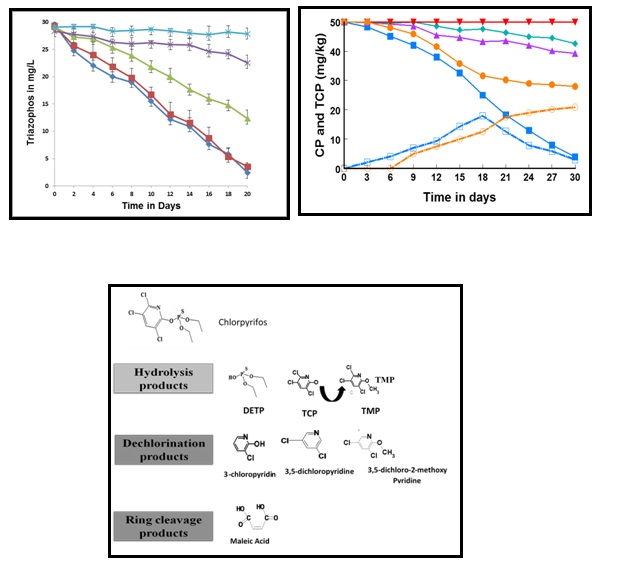
I am working in the area of bioremediation/biodegradation of pesticides contaminants whereby bacterial strains capable of degrading pesticides belonging to different chemical classes e.g. organophosphates, carbamates and pyrethroids have been isolated. The potential isolates have been characterized for their pesticides degradation potential in different culture conditions of water and soil microcosms spiked with pesticides. Metabolites of pesticides are identified during course of biodegradation by indigenous isolates.
PUBLICATIONS:
- S. Firdous, S. Iqbal, and S. Anwar, 2020. Optimization and modeling of glyphosate biodegradation by a novel Comamonas odontotermitis P2 through response surface methodology, Pedosphere, 30 (5) : 618-627.
- Wahla, A.Q., Anwar, S., Mueller, J.A. Iqbal, S., (2020). Immobilization of metribuzin degrading bacterial consortium MB3R on biochar enhances bioremediation of potato vegetated soil and restores bacterial community structure. Journal of Hazardous Materials. doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121493
- Ahmad, F., Ashraf, N., Da-Chuan, Y. Jabeen, H., Anwar, S., Wahla, A.Q., Iqbal, S. (2019) Application of a novel bacterial consortium BDAM for bioremediation of bispyribac sodium in wheat vegetated soil. Journal of Hazardous Materials 374: 58-65
-
- Wahla, A.Q., Iqbal, S., Anwar, S., Firdous, S. and Mueller, J.A (2019). Optimizing the metribuzin degrading potential of a novel bacterial consortium based on Taguchi design of experiment. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 366: 1-9
- Ahmad, F., Anwar, S., Firdous, S., Iqbal, S. and Yin Da-Chuan., (2018). Biodegradation of bispyribac sodium by a novel bacterial consortium BDAM: Optimization of degradation conditions using response surface methodology. Journal of Hazardous Materials 349:272-281
- S. Firdous, S. Iqbal, S. Anwar, and H. Jabeen, 2018. Identification and analysis of 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS) gene from glyphosate resistant Ochrobactrum intermedium Sq20,” Pest Manag Sci, 74(5):1184-1196.
- Jabeen, H., Iqbal, S., Anwar, S., Parales, R.E., 2015. Optimization of profenofos degradation by a novel bacterial consortium PBAC using response surface methodology. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 100: 89-97
- Shehzadi M., Afzal M., Khan M.U., Islam E., Mobin A., Anwar S., Khan Q.M. (2014). Enhanced degradation of textile effluent in constructed wetland system using Typha domingensis and textile effluent-degrading endophytic bacteria. Water Research. 58; 152-159.
- Jabeen, H., Iqbal, S. and Anwar, S. (2014). Biodegradation of chlorpyrifos and 3, 5, 6-trichloro-2-pyridinol by a novel rhizobial strain Mesorhizobium sp. HN3. Water and Environment Journal. doi: 10.1111/wej.12081.
- Ahmad, F., Anwar, S., Mustafa, T., Afzal, M., Khan, Q. M., Iqbal ,S. (2012). Enhanced remediation of chlorpyrifos from soil by using ryegrass (Lollium multiflorum) and chlorpyrifos-degrading bacterium Bacillus pumilus C2A1. J. Hazard. Mater. 110–115. HEC Best paper award
- Anwar, S., Liaquat, F., Khan, Q. M., Khalid, Z. M., Iqbal S. (2009). Biodegradation of chlorpyrifos and its hydrolysis product 3, 5, 6-trichloro-2-pyridinol by Bacillus pumilus strain C2A1. J Hazard. Mater. 168 (1): 400-405. HEC Best paper award
|