|
GoogleScholarProfile:https://scholar.google.com/citations?hl=en&user=nhFrPhIAAAAJ
ResearchGateProfile:https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Samina_Iqbal6
Research interests:
My main focus of research is development of microbial consortia for enhanced biodegradation and bioremediation of pesticides and related contaminants in agricultural soil and wastewater. Pesticide removal by rhizospheric and endophyticbacteria posseting pollutant degrading traits is a promising approach to all eviatecontaminant induced stress and increase remediation efficiency.The aim is to boost the degradation potential of the polluted matrix by using plant-associated bacteria and provision of nutrients and other amendments to enhance proliferation and activity of microbes.
Biodegradation and Bioremediation of insecticides:
Bacterialstrains and consortia capable of degradation of insecticides belonging to organ ophosphate,carbamate and pyrethroid groups have been isolated and characterized.Using various experimental designs e.g.“Response Surface Methodology”and“Taguchi Method”,process parameters formaximal degradation of pesticides have been optimize.Biodegradation of insecticides in vegetated/cropped soil and colonization of the inoculated bacteriains oil and plant tissues is investigated.Biodegradation pathways of someinsecticides by respective bacterial strain sand consortia have also been established.
Biodegradation and bioremediation of herbicides:
To cope with contamination of environment by ever increasing use of herbicides, timely remediation of such contaminants at point sourceis of utmost importance. The research work entails:1) isolation of bacteria (endophytes or rhizobacteria) capable of degrading herbicides inquastion;2) to determine the degradability of these herbicides in soil after application of the isolated bacteria; 3) colonization of the bacterial strains in the rhizosphere and inside plant tissues;4) effect of herbicides and inoculated bacteria on soil microbial communities and 5) development of inocular for bioremediation these herbicides in cropped fields. So far in ocular have been developed for bioremediation of bispyribac-Na, fluroxypyr, glyphosate and isoproturon and metrubuzin.
OTHER RESEARCH AREAS:
- Bio degradation/bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbons
- Biosorption/biodegradation of dyes present in textile effluents
- Enumeration/Detection of micro organisms in the environment
- Regulation of phosphonate degradation in Gram-negative organisms
SELECTED PUBLICATIONS:
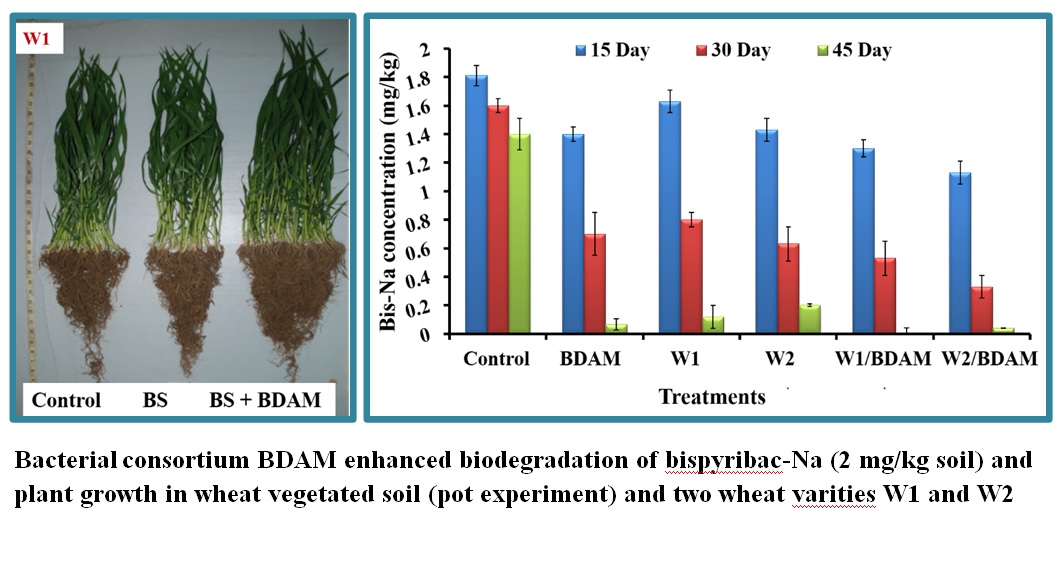
- Ahmad,F., Ashraf, A., Da-Chuan,Yin.,Jabeen, H., Anwar,S.,Wahla, AQ., and Iqbal., S.(2019) Application of a novel bacterial consortium BDAM for bioremediation of bispyribac sodium in wheat vegetated soil.J ournal of Hazardous Materials,In Press; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.03.130(I.F 6.434)
- Wahla,AQ.,Iqbal,S.,Anwar,S.,Firdous,S.,Mueller,J.2019.Optimizing the metribuz in degrading potential of anovel bacterial consortium based on Taguchi design of experiment.Journal of Hazardous Materials.366,1-9.(I.F6.434)
- Tahseen,R.,Khalid,Z.M.,Afzal,M.,Iqbal,S.,Arslan,M.,andAhmad,M.S.,(2019)Enhanced degradation of hydero carbons by gammaray induced mutants train of pseudo monasputida. Biotechnology letter(Inpress)(I.F1.846)
- Hussain,F.,Tahseen,R.,ArslanM.,Iqbal,S.,Afzal,M.(2019).Removal of hexa decane by hydroponic root mats in partnership with alkane-degrading bacteria: bacterial augmentation enhances system's performance.International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology.(inpress).(I.F.2.03)
- Shahid,M.J.,Tahseen,R.,Siddique,M.,Ali,S.,Iqbal,S.,Afzal,M.,(2018).Remediation of polluted river water by floating treatment wetlands.Water Science and Technology-Water Supply(inpress).(I.F0.674)
- Ahmad,F.,Anwar,S.,Firdous,S.,Da-Chuan,Yin.,andIqbal.,S.(2018) Biodegradation of bispyribacs odium by anovel bacterial consortium BDAM:Optimization of degradation conditions using response surface methodology.Journal of Hazardous Materials,5;349:272-281(I.F6.434)
- Firdous,S.,Iqbal,S.,Anwar,S.Jabeen,H.(2018).Identification and Analysis of 5-Enolpyruvylshikimate-3-Phosphate Synthase(EPSPS) Gene from Glyphosate Resistant Ochrobactrum intermedium Sq20.Pest Management Science.74(5):1184-1196.(I.F3.25)
- Hussain,Z.,Arslan,M.,Malik,M,H.,Mohsin,M.,Iqbal,S.,Afzal,M.(2018).Integratedperspective sontheuse of bacterial endophytes in horizontal flow constructed wetlands for the treatment of liquid textile effluent: Phytoremediation advances in the field.Journal of EnvironmentManagement.224:387-395.(I.F4.0).
- Hussain,Z.,Arslan,M.,Malik,M,H.,Mohsin,M.,Iqbal,S.,Afzal,M.,(2018).Treatment of the textile industry effluent in apilot-scale vertical flow constructed wet land system augmented with bacterial endophytes.Science of the Total Environment.645:966-973.(I.F4.610).
- Firdous,S.,Iqbal,S.,Anwar,S.2017.Optimization and modeling of glyphosate biodegradation by anovel ComamonasodontotermitisP2through response surface methodology.Pedosphere.Pedosphere201610546.R1.(IF1.74)
- Tahseen,R,.Afzal,M.,Iqbal,S.,KhanQ.M.Shabir,G.,KhalidZ.M.,Banat,IM.2016.Rhamnolipidsandnutrientsboostremediationofcrudeoil-contaminated soil by enhancing bacterial colonization and metabolic activities.International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation115,192–198.(IF2.45)
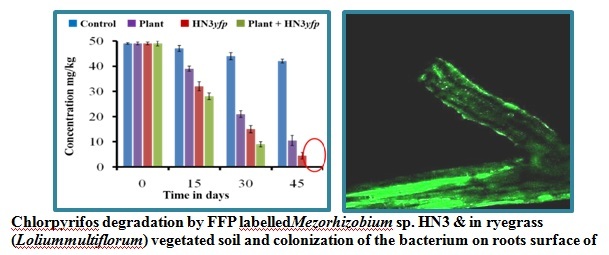
- Jabeen,H.,Iqbal,S.,Ahmad,F.,Afzal,M.2016.Enhanced remediation of chlorpyrifosbyrye-grass(Loliummultiflorum)andachlorpyrifosdegradingbacteriumMezorhizobiumsp.HN3.InternationalJournalofPhytoremediation.18:126-133.(IF2.45)
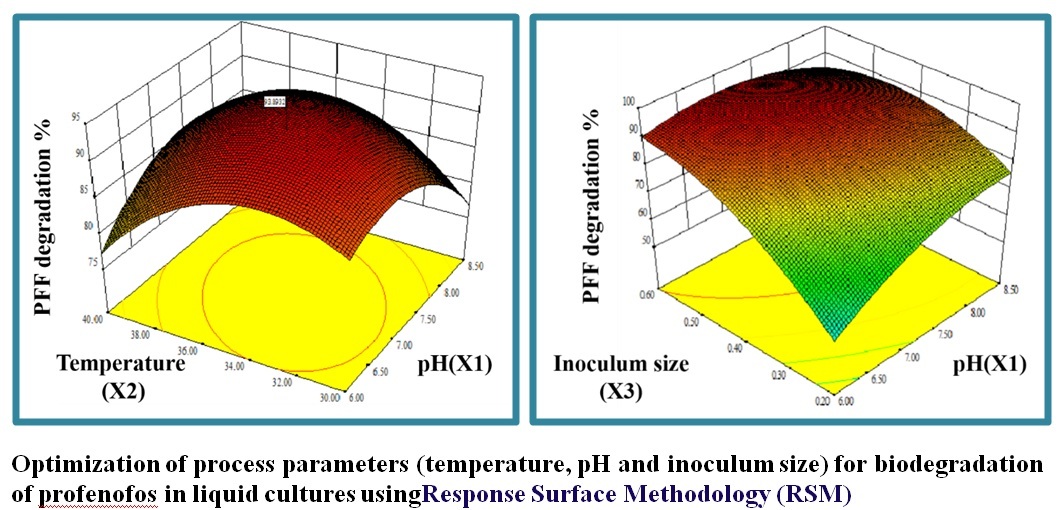
- Jabeen,H.,Iqbal,S.,Anwar,S.,Parales,RE.2015.Optimization of profen of osdegradation byanovelbacterialconsortiumPBACusingresponsesurface methodology.International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation100,89-97.(IF2.45)
- Jabeen,H.,Iqbal,S.,Anwar,S.2015.Biodegradationofchlorpyrifosand3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol by anovelrhizobialstrain Mesorhizobiumsp.HN3.Water and Environment Journal.151-160.
- Arslan,M.,Afzal,M.,Amin,I.,Iqbal,S.,Khan,QM.2014.Nutrients Can Enhance the Abundance and Expression of Alkane Hydroxylase CYP153 Geneinthe RhizosphereofRyegrass PlantedinHydrocarbon-Polluted Soil.PloSOne.9:e111208.
- Tara,N.,Afzal,M.,Ansari,T.M.,Tahseen,R.,Iqbal,S.,KhanQ.M.2014.Combin eduse of alkane-degrading and plant growth-promoting bacteria enhanced phytoremediation of dieselcontaminatedsoil.InternationalJournalofPhytoremediation.16:1268-1277.
- Afzal,M.,Shabir,G.,Iqbal,S.,Mustafa,T.,Khan,Q.M.,KhalidZ.M.2014.Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soil and ground water atleather industrial area of Kasur,Pakistan.CleanSoilAirandWater.42:1133-1139.
- Afzal,M.,Shabir,G.,Tahseen,R.,Islam,E.,Iqbal,S.,Khan,Q.M.,KhalidZ.M.2014.EndophyticBurkholderiasp.strainPsJNimprovesplant growth and phyto remediation of soilirrigated witht extile effluent.CleanSoilAirandWater.42:1304-1310.
- Afzal,M.,Khan,S.,Iqbal,S.,Mirza,MS.,KhanQM.2013.Inoculation method affects colonization and activity of BurkholderiaphytofirmansPsJNduringphyto remediation of diesel-contaminated soil.International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation.85:331-336.
- Khan,S.,Afzal,M.,Iqbal,S.,Miza,M.S.,KhanQ.M.2013.Inoculumpretreatment affects bacterial survival,activity and catabolic gene expression during phytoremediation of dieselcontaminated soil.Chemosphere.91:663-668.
- Shabir,G.,Afzal,M.,Tahseen,R.,Iqbal,S.,Khan,Q.M.,Khalid,Z.M.2013.Detoxification of oil refinery wastewater by pilot scale fedbatchreactor followed by coagulation and filtration.American Journal of EnvironmentalProtection.1:10-13.
- Khan,S.,Afzal,M.,Iqbal,S.,Khan,Q.M.2013.Plant-bacteri apartnerships for the remediation of hydrocarbon contaminated soil.Chemosphere90:1317-1332.
- Ahmad,F.,Iqbal,S.,Anwar,S.,Afzal,M.,Islam,E.,Mustafa,T.,Khan,Q.M.2012.Enhanced remediation of chlorpyrifos from soil usin gryegrass (Lolliummultiflorum) and chlorpyrifos-degrading bacterium Bacilluspumilus C2A1.J.Hazard.Mater.237-238:110-115.
- Anwar,S.,Liaquat,F.,Khan,QM.,Khalid,ZM.andIqbal,S.2009.Biodegradation of chlorpyrifos and itshydrolysis product 3,5, 6-trichloro-2-pyridinol by BacilluspumilusstrainC2A1.J.Hazard.Mater.168:400-40
|